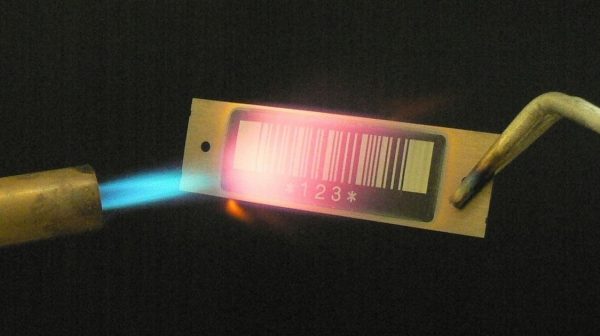
Industrial labelling refers to the creation and application of durable labels designed for use in industrial environments. These labels must withstand extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, moisture, chemicals, abrasion, and UV exposure. They often include barcodes, RFID tags, and other scannable technologies to facilitate tracking, traceability, and inventory management.
That’s the long and short of it! But if you’re reading a comprehensive guide to industrial labelling, you’ll probably want a little more information. In this blog we’ll cover the types of industrial labels, the key applications of industrial labels, the best practices of industrial labels, and more!
What makes an effective industrial label?
Labels are judged on much more than just their stickiness – particularly in industrial settings where the conditions are tough and the stakes are high. The following features are essential for industrial labels:
- Durability
Industrial environments are rarely gentle. From scorching heat in manufacturing plants to exposure to chemicals in laboratories or warehouses, labels must endure harsh conditions without degrading. A durable label maintains its integrity and functionality, ensuring vital information such as barcodes or instructions remains accessible.
- Customisation
Every industry has unique labelling needs, and a one-size-fits-all solution simply won’t suffice. Customisable labels are designed to meet specific requirements, whether it’s size, material, adhesive strength, or functionality. For example, some applications require tamper-evident labels to ensure product authenticity, while others may need RFID-enabled labels for efficient tracking.
- Readability
The purpose of a label is to communicate critical information, whether through barcodes, text, or symbols. High-resolution printing ensures that this information remains clear and legible, even after prolonged exposure to challenging conditions. Poor readability can lead to scanning errors, inefficiencies, or safety risks.
- Certifications
Compliance with industry standards is essential to ensure reliability and regulatory adherence. Certified labels, such as those meeting GS1, UL, or ISEGA standards, provide reassurance that the labels meet strict quality, safety, and hygiene criteria. For instance, GS1-certified labels are globally recognised for supply chain efficiency, while ISEGA certification is vital for labels used in direct food contact.
Types of industrial labels
There are several types of industrial labels, each with a unique set of features making them suitable for specific applications. They are labelled (see what we did there) thusly:
- Adhesive Labels
Adhesive labels are the workhorses of industrial labelling, prized for their versatility and adaptability. They can adhere to a wide variety of surfaces, from plastics and metals to glass and wood. Equipped with high-performance adhesives, these labels remain securely in place even under challenging conditions such as exposure to moisture, heat, or chemicals.
- Tamper-evident options: Certain adhesive labels are designed to reveal signs of tampering, adding a layer of security to valuable or sensitive goods.
- Applications: Ideal for inventory management, product identification, and temporary labelling where reapplication may be required.
- In-Mould Labels
In-mould labels take durability to the next level by becoming an integral part of the plastic they adorn. During the manufacturing process, these labels are fused into the plastic, creating a permanent, seamless marking solution.
- Durability: Their embedded nature ensures resistance to peeling, scratching, and environmental wear.
- Applications: Widely used in reusable systems where hygiene and longevity are paramount, such as food containers, pharmaceutical packaging, and transport bins.
- RFID Labels
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) labels are at the forefront of modern supply chain technology. Combining traditional barcode functionality with advanced contactless data transmission, these labels transform tracking and identification processes.
- Efficiency: RFID labels enable bulk scanning, allowing multiple items to be read simultaneously without direct line of sight. This reduces manual effort, speeds up inventory management, and minimises human error.
- Applications: Ideal for logistics, asset tracking, and environments where speed and precision are critical.
- Metal Labels
For extreme conditions, metal labels provide unparalleled resilience. These labels are designed to withstand high temperatures, corrosive chemicals, and physical wear, making them indispensable in demanding industries.
- Resilience: Made from durable materials like stainless steel or aluminium, metal labels maintain their integrity in environments that would compromise other label types.
- Applications: Commonly used in aerospace, heavy machinery, and industrial equipment requiring permanent identification under harsh conditions.
- Safety Labels
Safety labels are purpose-built to ensure clear communication of warnings, instructions, and regulatory compliance. Bright colours and bold designs make these labels highly visible, even in low-light or cluttered environments.
- Compliance: Many safety labels adhere to workplace standards, providing essential information for accident prevention and legal compliance.
- Applications: Found in manufacturing plants, construction sites, and any environment where worker safety is a priority.
Key applications of industrial labels
It’s easy to underestimate the worth of an industrial label. After all, is it not merely an identification tag that you slap on and then forget about? If only life were so simple. Industrial labels are, in fact, indispensable tools that enhance efficiency, safety, and traceability across various sectors. Here’s how they are applied in key industrial contexts:
- Asset Tracking
Tracking tools, machinery, and equipment is a cornerstone of efficient industrial operations. Labels, whether featuring barcodes, serial numbers, or RFID technology, assign unique identifiers to each asset.
Applications: Commonly used in factories, construction sites, and large facilities where managing numerous assets is a daily challenge.
- Inventory Management
Effective inventory management relies on accurate and accessible data, and industrial labels play a crucial role in this process. By incorporating barcodes or RFID tags, labels enable precise stock tracking.
Applications: Essential in industries such as logistics, retail, and manufacturing, where inventory turnover and accuracy are critical to success.
- Safety Compliance
Safety labels provide clear and durable warnings, instructions, and regulatory information to safeguard workers and ensure compliance with legal requirements.
Applications: Used for hazard warnings, machine operation instructions, and emergency signage in industries such as construction, oil and gas, and chemical manufacturing.
- Supply Chain Optimisation
Industrial labels are the backbone of efficient supply chains. They facilitate the seamless movement of goods, ensuring that items are tracked and accounted for at every stage of their journey.
Applications: Widely used in logistics, shipping, and distribution centres to improve visibility and accountability.
- IoT Integration
In the era of Industry 4.0, industrial labels have become key enablers of IoT (Internet of Things) integration. Labels link physical assets to their digital counterparts, enabling real-time monitoring and advanced analytics.
Applications: Found in smart factories, automated warehouses, and advanced manufacturing setups where interconnected systems drive productivity.
Best practices for industrial labels
Implementing effective industrial labelling requires careful planning and adherence to best practices to ensure labels perform reliably and meet operational needs. As the famous saying goes, “look after your labels and they will look after you.” Here are key considerations to guide your labelling strategy:
- Choose the right material
Selecting the appropriate label material is critical to ensuring longevity and functionality.
- Environmental considerations: Assess the conditions where the label will be applied. For instance, high-heat environments such as manufacturing plants may require durable metal labels that resist extreme temperatures, while cold storage facilities need moisture-resistant adhesives that maintain their hold in low temperatures.
- Application-specific materials: For industries like food or pharmaceuticals, consider materials that are hygienic and certified for safety.
- Prioritise durability
Durability is essential for labels used in industrial settings where they are exposed to wear and tear, chemicals, or environmental stressors.
- Longevity: Labels should retain their integrity, legibility, and functionality throughout their lifespan. Poor durability can lead to scanning errors, operational inefficiencies, or safety hazards.
- Protective features: Invest in labels with protective coatings or robust adhesives to prevent peeling, fading, or damage.
- Use standardised formats
Standardisation ensures compatibility and seamless integration within existing operational systems.
- Compliance: Opt for compliant barcodes or RFID systems, which are globally recognised and support efficient supply chain operations.
- Consistency: Standardised labelling formats improve readability and reduce errors during scanning or tracking processes.
- Regular maintenance and replacement
Even the most durable labels can experience wear over time, especially in demanding industrial environments.
- Inspection routines: Periodically check labels for signs of wear, fading, or damage. This practice ensures that the labels continue to serve their purpose without interruption.
- Proactive replacement: Replace any compromised labels promptly to maintain operational accuracy and safety.
- Leverage technology
Advancements in labelling technology can significantly enhance operational efficiency and data accuracy.
- Smart Labels: Invest in RFID-enabled labels for real-time tracking and automated data capture. These labels reduce manual effort, improve accuracy, and enable bulk scanning.
- IoT integration: Smart labels linked to IoT systems offer predictive maintenance, improved inventory management, and real-time asset monitoring, driving smarter decision-making across operations.
A sticky end…
And so concludes our in-depth foray into the world of industrial labels. Please ignore some of the more sarcastic remarks that were made throughout this article; believe it or not, we are actually quite passionate about a good label, and would happily discuss them with you at length.
If you have any questions or enquiries relating to inotec’s industrial labels, please contact us on 01482 654466 or info@inotec.co.uk.